Preparing for the NCLEX can feel overwhelming—especially when it comes to NCLEX lab values. The goal isn’t to memorize every number. It’s to recognize safe vs. unsafe ranges and choose the safest first action when values are off. Below is a focused guide to what you should know and how to study smarter.
Why NCLEX Lab Values Matter
Lab values drive safe nursing decisions. You’ll use them to:
-
Assess patient status and detect deterioration.
-
Monitor treatments (e.g., anticoagulation, diuretics, insulin).
-
Educate patients and families clearly and confidently.
On the NCLEX, labs appear inside case stems and trend items. Expect to identify the priority risk and choose an action that protects the patient now.
High-Yield NCLEX Lab Values (Know These Cold)
Tip: Focus on normal → danger → first action.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
-
Hgb: 12–16 g/dL (female), 14–18 g/dL (male)
-
Hct: 37–47% (female), 42–52% (male)
-
WBC: 4,500–11,000/mcL
Red flags: WBC <4,000 (infection risk), Hgb <8 (symptomatic anemia).
Likely actions: Infection precautions; oxygen, type & cross, provider notification based on symptoms.
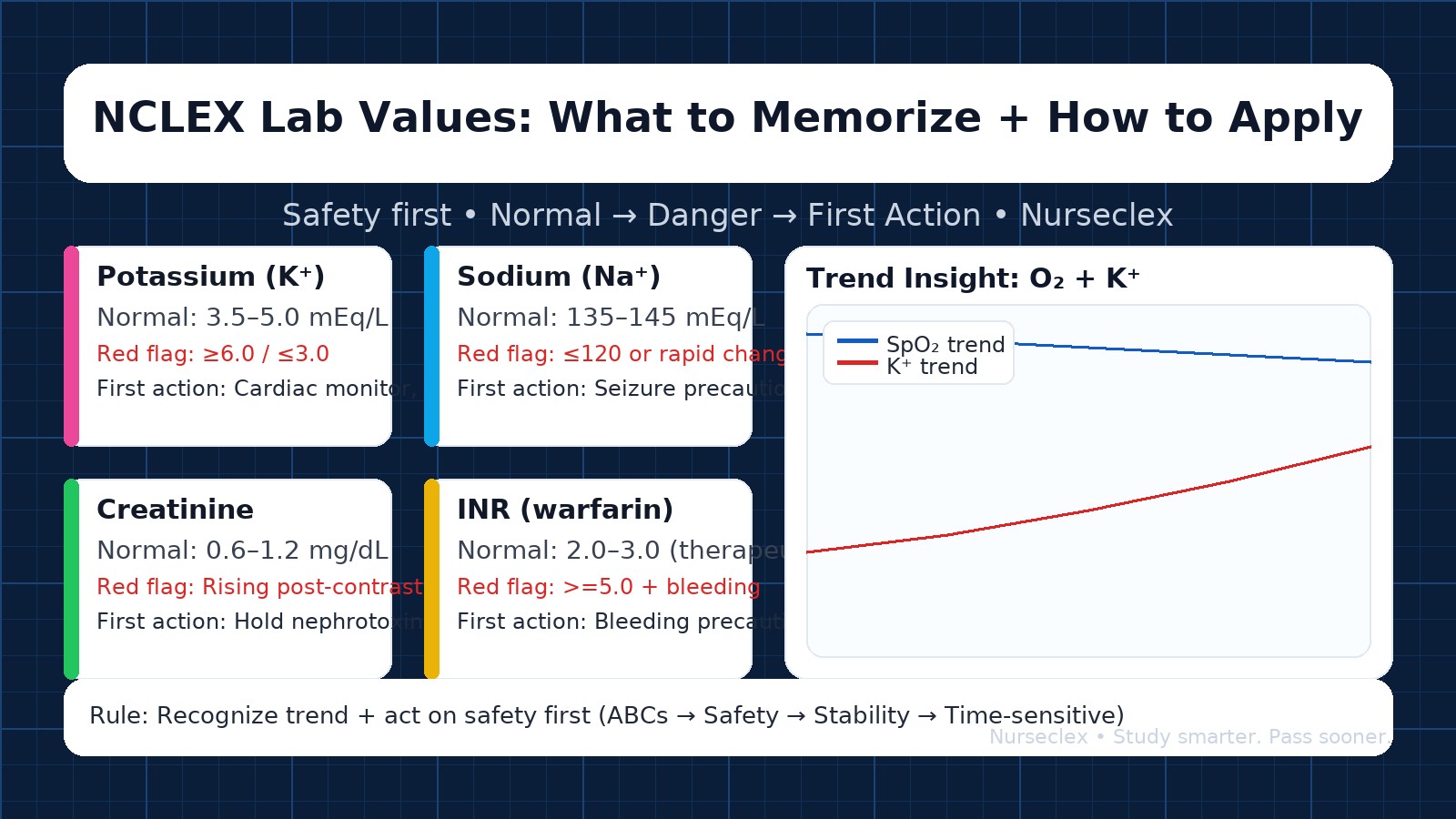
Electrolytes
-
Na: 135–145 mEq/L (neuro, seizure risk if low/rapid change)
-
K: 3.5–5.0 mEq/L (cardiac—watch for dysrhythmias)
-
Ca: 8.5–10.5 mg/dL (tetany if low; stones/“bones, groans” if high)
Red flags: K ≤3.0 or ≥6.0, ECG changes → cardiac monitoring, follow protocol; verify orders.
Kidney (Renal)
-
BUN: 7–20 mg/dL
-
Creatinine: 0.6–1.2 mg/dL
Red flags: Rising creatinine after contrast/aminoglycosides; UO <30 mL/hr → perfusion/renal risk.
Likely actions: I&O, hold nephrotoxins as ordered, provider notification.
Liver
-
AST: 10–40 U/L
-
ALT: 7–56 U/L
Red flags: Marked rises with RUQ pain/jaundice; evaluate meds (e.g., acetaminophen).
Coagulation (if tested)
-
INR: 2–3 (therapeutic warfarin range)
-
aPTT: ~60–80 sec (therapeutic heparin, per protocol)
Red flags: Oozing, tarry stools, hematuria.
Likely actions: Safety checks, reversal readiness (vitamin K, protamine), confirm orders.
Want a deeper drill by system? See NCLEX Pharmacology 2025 →
Do You Have to Memorize Every Value?
No. Prioritize core ranges and what to do when they’re out. The NCLEX rewards application:
-
Recognize trends (e.g., K 3.4 → 3.0 → 2.8).
-
Match the safest immediate action (monitor, hold, notify, treat).
-
Stabilize before you teach.
Fast, Proven Study Strategies
1) Smart mnemonics (only for the essentials)
Use short anchors, then tie them to first actions.
-
K = 3.5–5.0: “3–5 bananas on the counter → heart rhythm”
-
Na = 135–145: “135–145 keeps the brain alive”
2) Flashcards with “danger + action”
Front: K 6.2.
Back: Danger: ventricular dysrhythmias; Action: cardiac monitor, verify ECG, follow hyperK protocol.
3) Practice questions (daily)
Mix short sets with rationales. Tag misses as content or strategy and retest within 24–72 hours.
Try mixed blocks in Nurseclex →
4) Case-style thinking
Read the stem twice. Name the priority problem. Choose the safest first action.
Sharpen this with Analysis & Prioritization →
5) Build a one-page cheat card
Columns: Lab → Normal → Red Flag → First Action. Recopy weekly to cement recall.
Mini Quick-Checks You’ll See on NCLEX
-
K ≥6.0 with peaked T waves? Cardiac monitor now; follow protocol.
-
Na 120 with confusion? Seizure precautions; provider notification.
-
Cr rising after contrast? Hold nephrotoxins as ordered; assess I&O, fluids.
-
INR 5.0 + gum bleeding? Bleeding precautions; verify orders; anticipate reversal.
Where This Fits in Your Plan
-
Weekdays: 10–15 min lab drills + 15–25 mixed questions.
-
Weekends: 1 full CAT session with labs embedded.
-
Track: Missed labs → add to cheat card → retest in 24–72 hrs.
Bottom Line
You don’t need to memorize every lab value for the NCLEX. You do need to know the core ranges, spot danger, and choose the safest first action. Practice in context and you’ll be ready.
Get targeted drills, rationales, and CAT sims built for real clinical judgment at Nurseclex. Start with Nurseclex → and build your one-page lab card today.